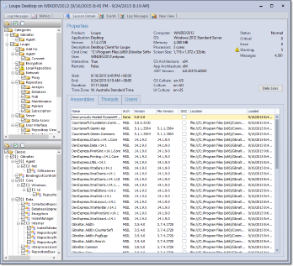
The Session Details tab of the session viewer contains:
- Session Details: Information about the specific application, computer, and the processing environment.
- Threads List: Information on each thread that recorded at least one log message in the process.
- Assemblies List: Information on every assembly that was loaded into the process.
- Users List: Information on each application user that was recorded in the session.
This information is particularly useful when comparing a session that experienced a problem with others that didn't - often the difference is caused by an attribute of the processing environment that is different, such as a dependent assembly or process architecture.
Session Details |
Session Properties
Many properties are captured for each session. Of particular interest are:
Process Architecture
While .NET generally handles architectural differences automatically there are situations when problems can arise. For backwards compatibility reasons, newer 64 bit architectures (IA64 and Amd64) still support running processes as 32-bit applications (X86). The session details includes the .NET Architecture and computer architecture so you can determine what the native architecture of the operating system was and what the effective architecture of the process was. Architecture also shows up in the assembly list, indicating whether a particular assembly was targeted at just one architecture or was compiled as MSIL which can be used in any architecture.
Culture
Often, an application is developed and tested exclusively on a single culture (like United States English, which has the unique name "en-US") and then encounters unexpected errors when run on an alternate culture. There are multiple cultures that come into play:
- Operating System Culture: The native culture the OS was installed or is currently operating in (Windows XP and earlier operating systems determined primary culture during installation, Vista and later have a single installation that allows culture selection). Native calls will respective this culture.
- Culture: The primary process culture (in .Net the CultureInfo.CurrentCulture property). Most .NET software runs against this culture by default.
- User Interface Culture: The foreground UI culture can be changed dynamically and affects user interface components.
While some of these cultures can conceptually change during the execution of a process, the initial culture is captured and reflected in the session details.
Threads
A list of all of the threads that logged any message. Other threads may have existed in the .NET process that didn't log any messages and therefore weren't recorded. For each thread, the following information is captured:
- Id: The unique numerical ID of the thread within the process
- Name: A display name assigned to the thread, if any was. Names are not necessarily unique.
- Background: Indicates if the thread was set up as a background thread. Background threads do not have user interfaces and will not keep a process running.
- Pool: Indicates if the thread was part of the .NET thread pool. All pool threads are background threads.
Assemblies
Every assembly that was loaded into the process is listed. For each assembly that was loaded, the following information is captured:
- Assembly Name: The declared name of the assembly (this may not be unique).
- Culture: If an assembly is associated with exactly one culture it will be listed. Most assemblies target the neutral culture which displays as an empty value in this column.
- Architecture: The process architecture targeted by the assembly. Most assemblies target MSIL which can be dynamically recompiled to the process' current architecture at runtime.
- Version: The assembly version. This is used by the .NET runtime to validate version compatibility of versions.
- File Version: The file version of the assembly, if it could be determined. Because changing the assembly version indicates a potential compatibility problem, many updated assemblies will change just the file version unless a change is made to the public interface of the assembly.
- Image CLR Version: The version of the .NET Common Language Runtime targeted by the assembly. As of .NET 2.0 it's possible to have a mix of CLR versions targeted in the same process, ranging from .NET 2.0 through 4.0.
- GAC: Indicates if the assembly was loaded from the Global Assembly Cache or not.
- Location: The location of the assembly binary on disk.
Users
If an application recorded information from multiple users (including the process user) then the Users panel is displayed with the list of the details available for each user. If an application provides extended Application User information this will be displayed here, making it easy to test exactly what was provided by the application at runtime.